Realm API Keys #
Configuring the CoSync AssetLink or CoSync Auth services for a MongoDB Realm Application is very easy, as long as the developer has created and gathered the appropriate Realm API keys for the process to take place.
What is a programmatic key? #
A programmatic key has both a public key and a private key associated with it. The developer must save the private key at the time a programmatic key is defined because it is not retrievable after the fact. The developer is responsible for safe guarding this private key; the CoSync Portal will use the public/private key pair to configure a MongoDB Realm Application but never save this pair to its data-base. Rule: CoSync never stores the developer’s Atlas public/private keys in its database, meaning it cannot provide assistance if the developer misplaces or loses them.
What you will need #
To configure the CoSync Auth service, the developer will need to gather
- MongoDB Realm Application Id,
- MongoDB Realm Project Id,
- Realm project or organization Public API Key,
- Realm project or organization Private API key.
This may seem like a lot of information for the developer to gather, but on the plus side it only needs to be done once during configuration. As a rule, the CoSync Portal never stores any private key information. Rather it uses the keys passed in to configure the MongoDB Realm Application for the various CoSync services and discards them afterwards.
We detail in the following section how the developer should go about gathering and/or creating these keys for use by the CoSync Portal. The API keys that are gather are very sensitive and the developer should adopt the utmost care to keep them secret from the outside world. As a best practice, these keys should be stored on a separate USB key in an encrypted file, and/or with a printed copy put in a safe.
In order for the CoSync Portal to be able to configure a MongoDB Realm Application for the CoSync AssetLink or CoSync Auth services automatically, the developer must first setup a set of programmatic API keys for either the organization or the project that the MongoDB Realm Application belongs to. Programmatic API keys are explained in the MongoDB Documentation.
The topology of MongoDB Atlas organizes everything under an organization that is associated with a developer account. An organization can contain a number of projects that in turn can contain a number of Atlas Clusters and/or MongoDB Realm Applications associated with them. Programmatic keys enable an outside program (like the CoSync Portal) to call into MongoDB and configure a MongoDB Realm Application through the Realm Administration API.
Get Realm Application ID #
For any type of configuration of a MongoDB Realm Application, the developer will need to get the Realm Application Id from the MongoDB Realm Portal. Fortunately, MongoDB makes this task very easy.
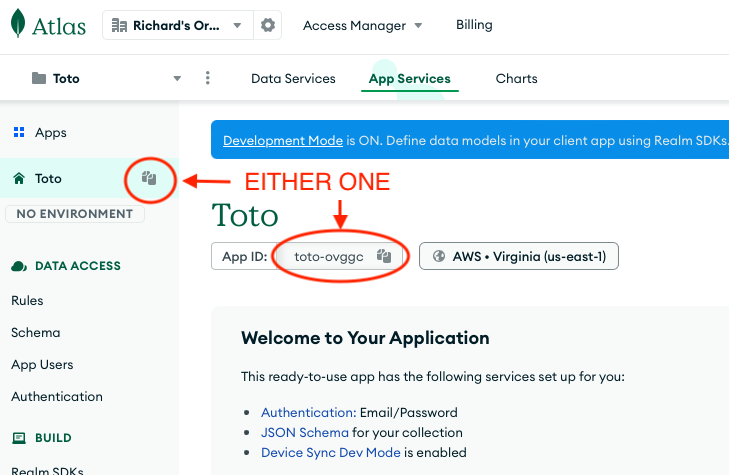
In the top left corner of the user interface, MongoDB Realm presents a Copy App ID icon that will copy the Realm Application Id (in this case ’estapplication-ukvsm’) to the clipboard.
Get Realm Project ID #
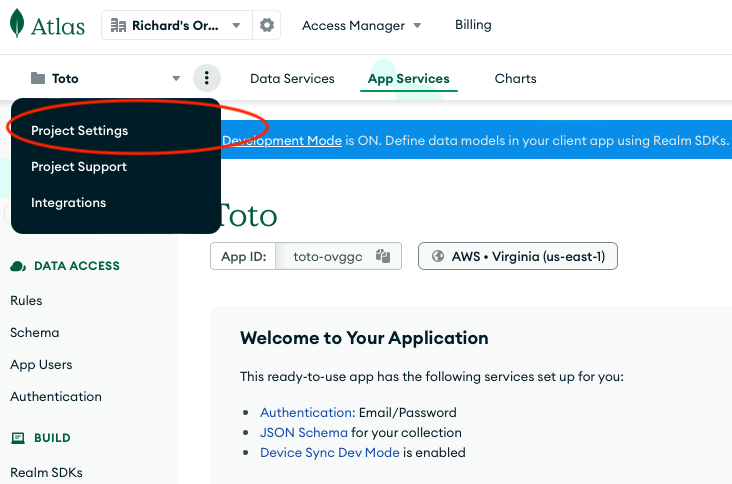
MongoDB Altas organizes Atlas Clusters and MongoDB Realm Application underneath projects, that exist in turn underneath an organization. A project has a unique Project Id that can be retrieved by going to the Project Settings underneath the three vertical dot menu next to the Realm Application Id in the top left corner.
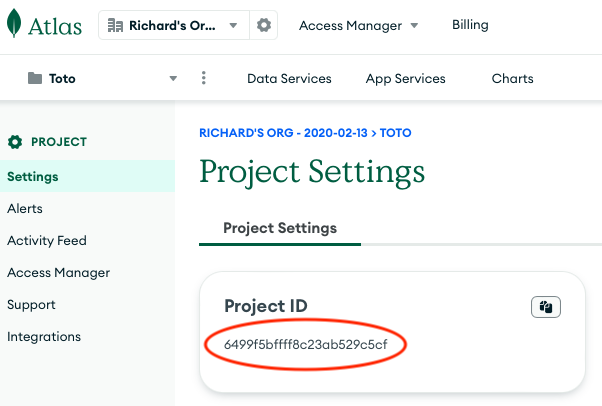
After the developer brings up the Project Settings, the portal will display a page with the Project ID an a hexadecimal string. The developer should copy this Project Id to a separate file to be used in the configuration of the CoSync Auth and CoSync AssetLink services for a MongoDB Realm Application.
How to create a programmatic key #
Creating a programmatic key is easy. First, from the MongoDB Realm Portal, the developer should select Access Manager from the top menu. In our example, the developer should create programmatic key that is specific to the project, so should select Project Access from the menu. Organization keys have the added advantages of working across projects for the entire developer account, they do however pose a greater security threat, should they be leaked out. Best practices would suggest that keys should be limited to the project per se, not the organization in general.
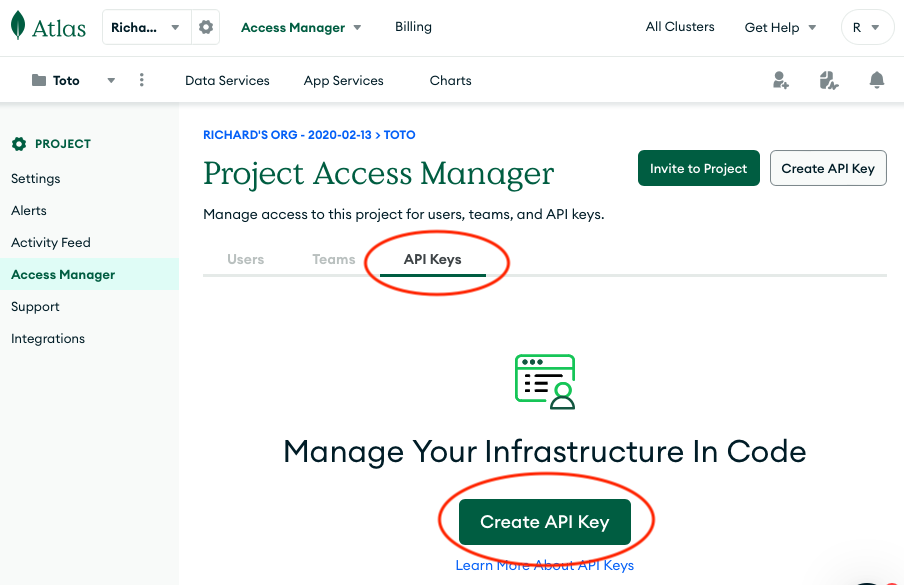
Second, the developer should select the API Keys tab and select Create API Key.
Get Public Key #
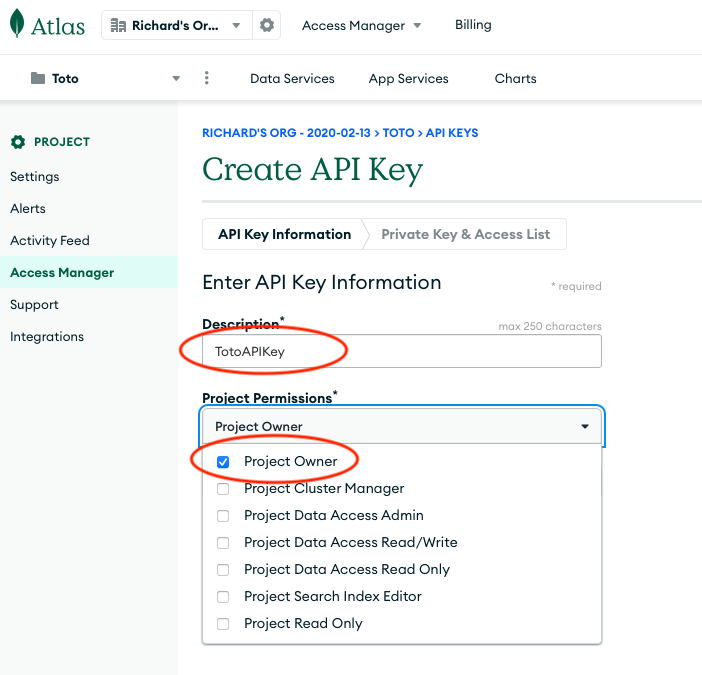
Third, before the developer can create the programmatic key, he/she must make sure that Project Owner is selected under Project Permissions. The developer should also copy the Public Key to a separate file for safekeeping.
Get Private Key #
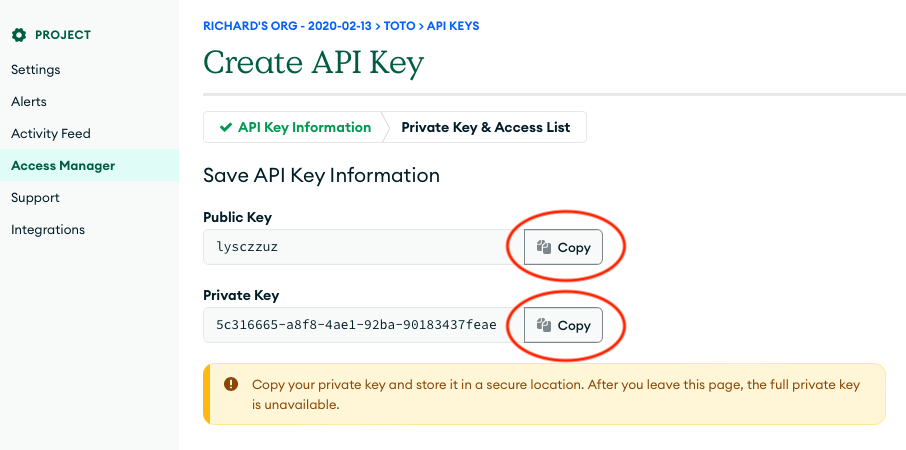
Fourth, after the private key is created, the developer should save it away for safekeeping. It is not retrievable after this point.
At this juncture, the developer has created a programmatic key for the CoSync Portal to configure the MongoDB Realm Application programmatically for the CoSync AssetLink or CoSync Auth services.
Public & Private Keys - The developer must save both the public and private keys in a separate file for the configuration process. These keys are effectively API passwords to the MongoDB Realm account, so should be guarded with the same level of scrutiny as an admin password. Our suggestion would be to save them to an encrypted USB key fab for safekeeping.
Get Service ID #
The developer will need to gather the same keys for configuring the CoSync AssetLink service, but also gather an additional key:
The Service Id is only used for CoSync AssetLink, it does not apply for CoSync Auth
To be able to configure the CoSync AssetLink module for a MongoDB Realm Application, the developer will need to retrieve the Realm Service Id for the associated MongoDB Atlas cluster. The Realm Service Id is needed by the CoSync Portal to install server-side functions in to the MongoDB Realm Application remotely. Unfortunately, this identifier is a little harder to retrieve from the Realm Application Portal - but not impossible.
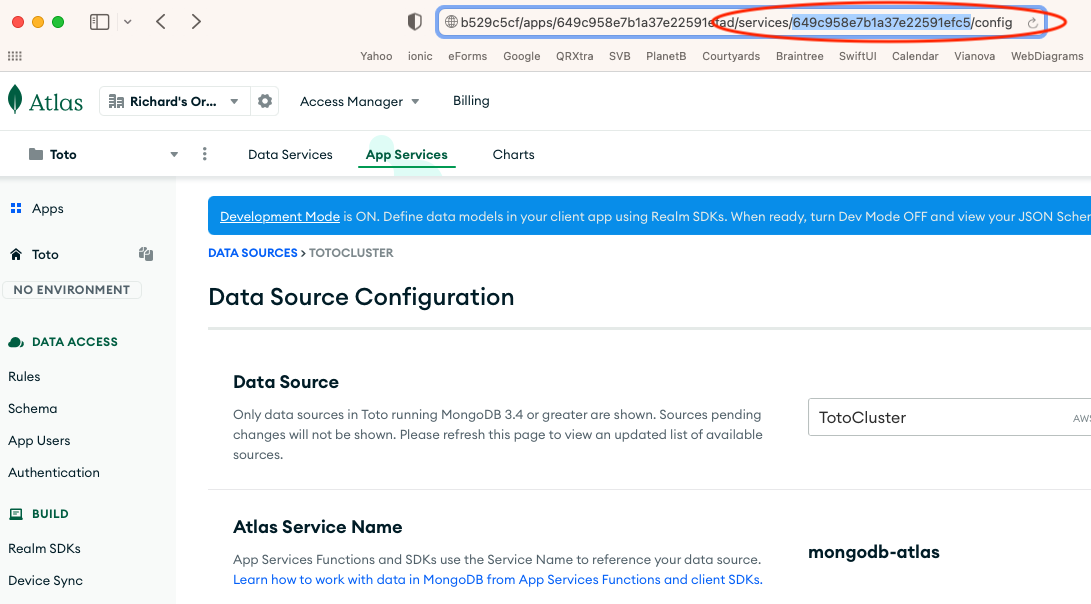
In the example shown below, the Service Id is equal to ‘649c958e7b1a37e22591efc5’.
First, the developer should go to the Linked Data Sources section of the MongoDB App Services portal, as shown below.
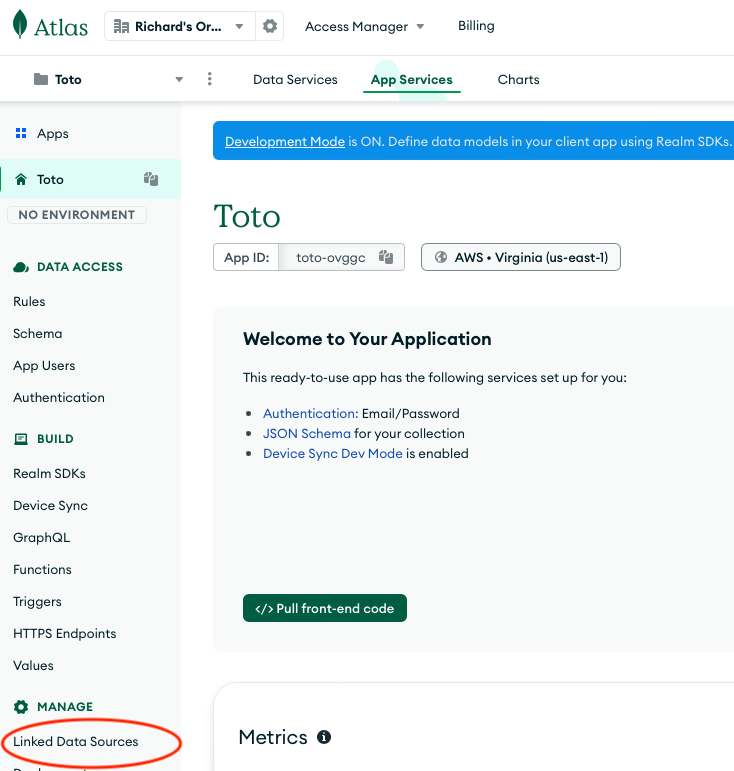
Second, the developer should click on the service name ‘mongodb-atlas’ to bring up the data source services.
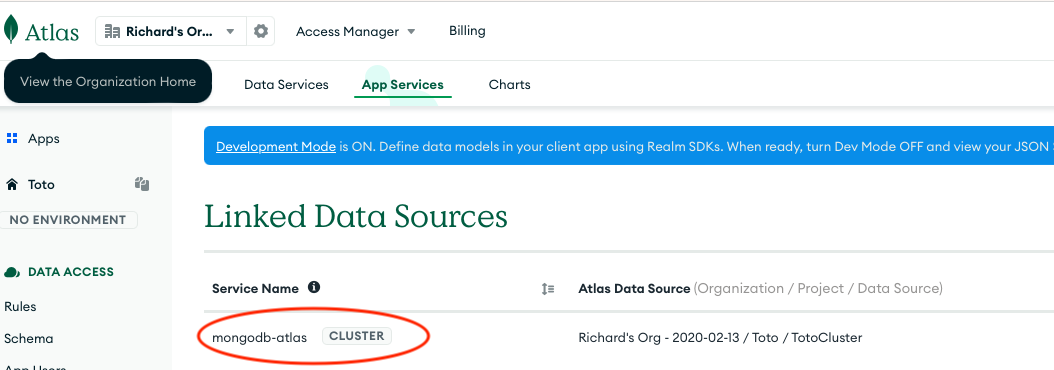
Third, the developer should go to the browser window address bar and scroll all the way to the right. Then the developer should copy the hexadecimal string between the path component services and the path component config - in our example ‘649c958e7b1a37e22591efc5’. This is the Service Id for the MongoDB Realm Application - Toto - that should be saved to a separate file for the configuration of the CoSync AssetLink module.